EOR vs. PEO - Pros and Cons
Magnit July 31 2023

Managing workforces is getting more and more complex, especially as more companies are relying on remote and international workers to help optimize their talent supply chain. Depending on the type and size of the business, companies may partner with a Professional Employer Organization (PEO) or an Employer of Record (EOR) to help manage HR functions and remain compliant with local employment laws and regulations. But how can organizations determine which is better for the needs of their business?
In this blog post, we’re going to cover:
1. The difference between an EOR and PEO
2. The advantages of using a PEO
3. The disadvantages of using a PEO
4. The advantages of using an EOR
5. The disadvantages of using an EOR
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
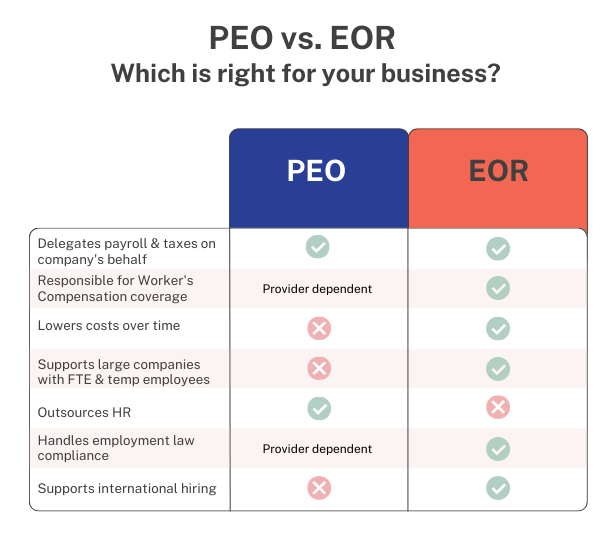
What's the difference between an EOR vs. PEO?
PEO (Professional Employer Organization)
A Professional Employer Organization (PEO) is a third-party service provider that offers human resources (HR) solutions to businesses. PEOs are typically responsible for managing essential HR functions, which include payroll management, employee benefits administration, workers’ compensation and some compliance services to ensure companies abide by employment laws. Through their co-employment arrangements, PEOs assume certain responsibilities on behalf of the businesses they work with, allowing companies to focus more on other operations while the PEO handles their HR needs.
EOR (Employer of Record)
An Employer of Record (EOR) is an organization that handles the responsibility of managing and administering payroll, risk management, and benefits for the employees at a company on the businesses’ behalf. Working with an EOR enables organizations to outsource payroll processing, risk mitigation tasks, and benefits administration. The EOR also assumes the crucial task of making sure local labor laws are followed, abiding by laws, staying up to date on the most recent legal requirements and changes, administering employee benefits and compensation, and putting preventative measures in place to reduce compliance risk. EORs deliver compliance guidance holistically across multiple categories of labor that are ongoing, versus being specifically focused on engagement (or hire) by engagement basis. EORs are essentially the experts in compliance at regional and local levels, guiding their customers to the best scalable solutions in related regions and beyond.
With a co-employment engagement through a PEO, the PEO and business still split certain responsibilities. An EOR, on the other hand, handles all the employer responsibilities on behalf of the organization.
Advantages of Using a PEO
Businesses can gain a lot of benefits by working with a PEO. These include having access to specialized HR knowledge and obtaining employee perks and insurance at affordable costs. By utilizing the PEO's expertise and experience, businesses can minimize administrative procedures and concentrate on their main business operations. Depending on the PEO, it can help guarantee that employment laws are followed, lowering legal risks and offering assistance when navigating complex legislation.
Additionally, PEOs offer employee benefit packages and provide scalability and flexibility, assisting firms in adjusting to fluctuating worker needs. Lastly, PEOs help to reduce the risks related to liability insurance, workers' compensation, and employment practices.
Disadvantages of Using a PEO
Using a PEO brings businesses advantages, but potential disadvantages should be considered. These include a loss of control over HR functions, limited customization options, dependency on a third-party provider, additional costs, potential communication challenges, and limited control over decision-making.
Co-employment arrangements may also cause confusion among employees regarding roles and responsibilities. Furthermore, there is a possibility of disruption if the provider is unable to meet expectations or faces financial instability. And because PEOs don’t assume all compliance risks, they can limit a company’s ability to efficiently expand into new locations.
If the pricing model of the PEO is based on the percentage of monthly payroll spend, costs may rise as more payroll spend gets added. Depending on the provider, extra percentages can incur if payroll grows by a specific variable in one month as well. Customers also get less input on benefit plans and schemes, which may include additional costs.
When selecting a PEO, it is crucial to carefully evaluate it and weigh the benefits against these potential drawbacks and ensure alignment with the company's needs and HR management requirements.
Advantages of Using an EOR
Working with a leading-edge EOR provides organizations with numerous benefits, including:
- Partnering With a Trusted Advisor: EORs act as a partner to the organizations they support as opposed to a vendor. They are actively involved in continual improvement and move quickly with the business as opposed to acting as an independent employer. For example, Magnit’s EOR services, including compliance, benefits, consulting and more, are all integrated under a single umbrella versus the piecemeal approach from a PEO, providing a holistic view into the organization and enabling it to remain flexible amidst shifting circumstances and business needs.
- Increased Cost Savings: By avoiding agency markups, an EOR can assist the organization in lowering costs associated with each engagement with a worker. Additionally, EOR service providers like Magnit lower program costs by giving businesses complete data visibility integrated with market intelligence, enabling them to make cost-effective hiring and retention decisions. See how Magnit EOR can help your business achieve world-class cost savings in our infographic.
- Better Risk Mitigation: EORs reduce risk to the company by taking on the legal responsibilities of managing payroll, taxes, and HR as well as ensuring compliance with local legislation. By doing this, the company is further safeguarded against co-employment risk-related litigation and financial penalties.
- Meeting Compliance: An EOR provides legal expertise for businesses, including those operating in different places and countries, to fulfill all regulatory compliance needs, which can include support, education, standardizing processes, visibility into total spend and more. Because of their expertise and role in meeting local compliance regulations, partnering with an EOR is also especially crucial for organizations looking to expand their talent pools and hire globally.
- Enhanced Worker Experience: The worker experience within an organization can be greatly enhanced with the proper EOR partner through health and wellness benefits, 401k and pension plans, and even real-time, on-demand pay and more.
Learn more about the advantages of partnering with an EOR provider in our EOR comprehensive guide.
Disadvantages of Using an EOR
Using an Employer of Record (EOR) can come with some potential challenges. Depending on the provider, it could be more costly in the short-term compared to handling employment tasks in-house. Outsourcing employment responsibilities also means losing some control over the workforce, which could create obstacles.
In addition, cultural mismatches may arise if the EOR operates in a different country or region, which could potentially impact employee communications or create challenges when working with an EOR in a different time zone. That is why it is essential for organizations to carefully research and discuss any questions and concerns with the EOR they are considering to ensure it is the best fit.
FAQs
- What’s the key difference between an EOR and a PEO?
The biggest difference between PEO co-employment and EOR is that through a PEO, there are still shared responsibilities between the PEO and the business. Full employment through the EOR, on the other hand, transfers all employer responsibilities to the EOR provider, making it the legal employer of the worker. Smaller businesses may utilize co-employment through a PEO for their expertise, while businesses with global or remote workforces may partner with an EOR to help them navigate local and international regulations more effectively.
- How do EOR and PEO services differ in terms of legal requirements?
Under an EOR arrangement, the EOR becomes the legal employer of the workers and assumes all responsibility to comply with employment laws, tax regulations, and other legal obligations associated with employment. The EOR also manages payroll taxes, employment contracts, benefit administration, ensures compliance with local labor laws.
With the PEO model, the PEO and company share legal obligations as co-employers. While the PEO assists with HR duties and administration, the client company maintains control over daily operations and is still in charge of adhering to employment laws. While PEOs and EORs have different legal obligations, the EOR holds greater legal responsibility as it servers as the employer of record.
- What’s the main disadvantage of using a PEO compared to an EOR service?
The division of legal responsibilities is the greatest disadvantage of utilizing a PEO. The nature of the PEO co-employment arrangement holds the client company liable to abide by employment laws and regulations. This can potentially create some complexities and potential risk for the company. On the other hand, an EOR partner takes on full legal responsibility since it serves as the employer of record, which completely relieves the client company of those responsibilities.
- Should I use an EOR or PEO when hiring internationally?
An EOR is the best choice for organizations that are hiring workers globally. EORs are the experts in staying on top of employment laws and regulations across various locations and countries. In addition, EORs offer flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to easily grow their operations abroad without forming legal entities in every jurisdiction. Last but not least, by using an EOR, businesses may reduce the dangers connected to unfamiliar employment regulations and cultural differences, allowing them to assure efficient and legal operations in international labor markets while expanding their talent pools.
Although PEOs and EORs may perform some similar functions, they handle them differently and to different capacities. That is why it is important to fully understand how each aligns to your organization, so you can choose the best fit and partner for your unique business.
To find out how Magnit EOR can help achieve $11.2 million in cost savings over three years, download our Forrester Total Economic Impact report.
Disclaimer: The content in this blog post is for informational purposes only and cannot be construed as specific legal advice or as a substitute for legal advice. The blog post reflects the opinion of Magnit and is not to be construed as legal solutions and positions. Contact an attorney for specific advice and guidance for specific issues or questions.